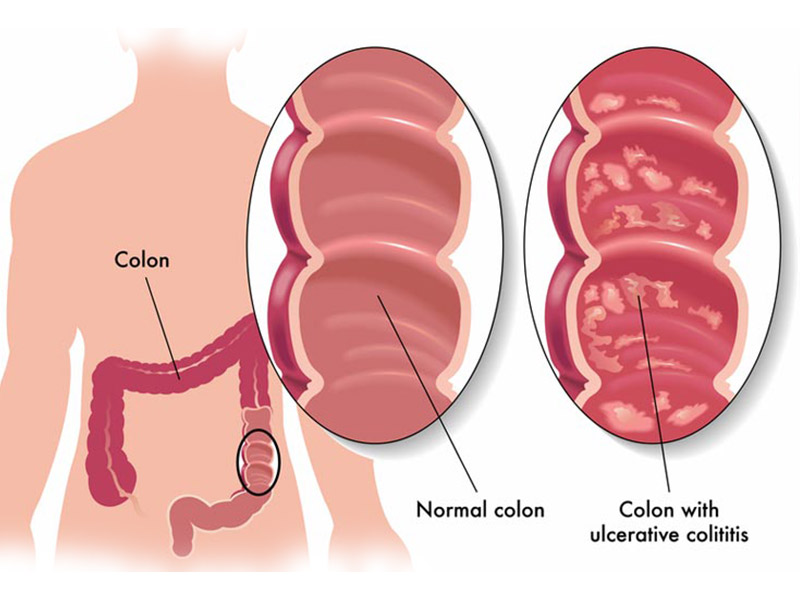
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UL-sur-uh-tiv koe-LIE-tis) is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes inflammation and ulcers (sores) in your digestive tract. Ulcerative colitis affects the innermost lining of your large intestine (colon) and rectum.
What are the Symptoms?
Symptoms usually develop over time, rather than suddenly. Symptoms of ulcerative colitis tend to differ from one person to another.
Some of the common signs of Ulcerative colitis are:
- Abdominal Pain
- Blood in the stools
- Diarrhoea
- Mild fever
- Pain in the rectum
- Unintended weight loss
- Malnutrition
- Pain and/or inflammation in the joints
- Loss of appetite
- Mouth sores
- Inflammation in the eyes
What are the Causes?
Ulcerative Colitis occurs when the immune system attacks its own body. The white blood cells instead of protecting the lining of the large intestine, begin to attack it causing inflammation & ulcers. There is no conclusive evidence as to why ulcerative colitis t. While genes may play a role, certain factors in the environment may also cause this disease.
How is it Diagnosed?
- Blood tests to check for anemia or inflammation
- Stool test to detect if there is an infection or parasite in the colon
- Sigmoidoscopy
- Colonoscopy
- Biopsy
- CT Scan
What are the Risk Factor?
- Age: Ulcerative Colitis commonly occurs in individuals of age group 15 to 30 years and those above 60.
- Family History: Risk increases in individuals who have a parent or sibling with this disease.
- Immune Disorders: If a person has one type of immune disorder, chances of developing a second one are pretty high
- Bacterial or viral infections may trigger the immune system
Possible complications of ulcerative colitis include:
- Severe bleeding
- A hole in the colon (perforated colon)
- Severe dehydration
- Bone loss (osteoporosis)
- Inflammation of your skin, joints and eyes
- An increased risk of colon cancer
- A rapidly swelling colon (toxic megacolon)
- Increased risk of blood clots in veins and arteries
How is it Treated?
Treatment for Ulcerative colitis involves a combination of medications and dietary changes. In some cases, a surgical intervention may be necessary
- Diet: Doctors recommend a balanced diet with lots of fruits & vegetables to ensure the patient receives enough vitamins, minerals & other nutrients.
- Medications: Your gastroenterologist may recommend a combination of the medications such as
- Antibiotics
- Corticosteroids
- Immunomodulators
- Biologics
- Other medications for diarrhoea Surgery: A proctolectomy may be recommended in case other treatment methods do not work. Proctolectomy refers to surgical removal of the colon & rectum