Hepatitis C
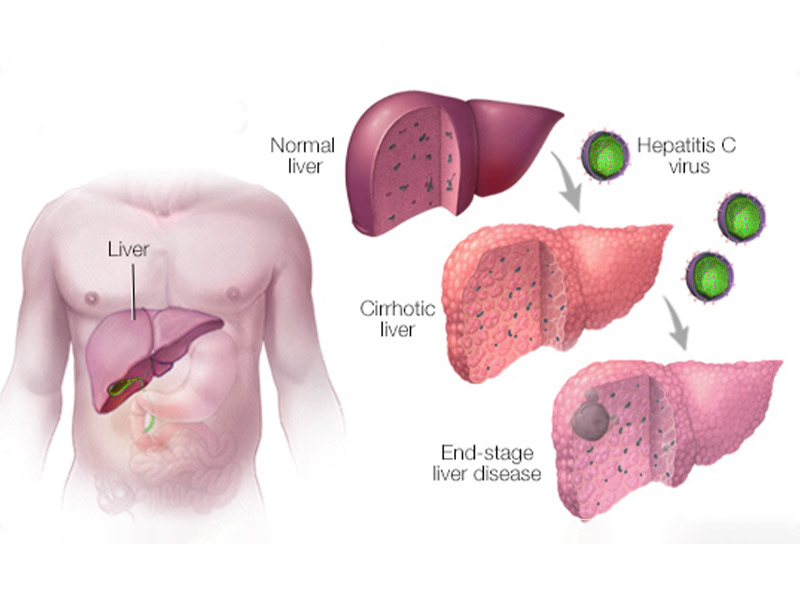
Hepatitis C is a medical condition caused by the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). It is a highly contagious disorder. But it only spreads through contaminated blood and not through casual contact.
What are the Symptoms?
Most patients with hepatitis C present no symptoms. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Bleeding Easily
- Bruising Easily
- Fatigue
- Poor Appetite
- Jaundice
- Dark Coloured Urine
- Itchy Skin
- Swelling in your legs
- Weight loss
- Confusion & slurred speech
What are the Causes?
Hepatitis C infection is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection spreads when blood contaminated with the virus enters the bloodstream of an uninfected person.
Globally, HCV exists in several distinct forms, known as genotypes. Seven distinct HCV genotypes and more than 67 subtypes have been identified. The most common HCV genotype in the United States is type 1.
Although chronic hepatitis C follows a similar course regardless of the genotype of the infecting virus, treatment recommendations vary depending on viral genotype.
How is it Diagnosed?
Screening for hepatitis C: All adults ages 18 to 79 years be screened for hepatitis C, even those without symptoms or known liver disease.
Blood tests: Hepatitis C is usually diagnosed using 2 blood tests: the antibody test and the PCR test. The results usually come back within 2 weeks. If an initial blood test shows that you have hepatitis C, additional blood tests will:
- Measure the quantity of the hepatitis C virus in your blood (viral load)
- Identify the genotype of the virus
Ultrasound scans: Where sound waves are used to test how stiff your liver is; stiffness suggests the liver is scarred
What are the Risk Factor?
Your risk of hepatitis C infection is increased if you:
- Are a health care worker who has been exposed to infected blood, which may happen if an infected needle pierces your skin
- Have ever injected or inhaled illicit drugs
- Have HIV
- Received a piercing or tattoo in an unclean environment using unsterile equipment
- Received a blood transfusion or organ transplant before 1992
- Received clotting factor concentrates before 1987
- Received hemodialysis treatments for a long period of time
- Were born to a woman with a hepatitis C infection
- Were ever in prison
- Were born between 1945 and 1965, the age group with the highest incidence of hepatitis C infection
How is it Treated?
Not every patient infected with Hep C virus needs a treatment. For most people, body’s immune systems are able to fight off the infection. In such cases, your doctor may recommend regular blood tests to monitor liver function.
In patients with weaker immune systems, doctor may recommend certain medications to treat the infection. Some of the medications include interferon & antivirals. Your doctor has to first identify the Hepatitis C genotype to have a better clarity of what medications work the best.