Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a digestive disorder in which the stomach acid flows back into the Esophagus. Esophagus is the tube like structure connecting the mouth with the stomach. The acid reflux or the back flow of acid irritates the lining of the Esophagus.
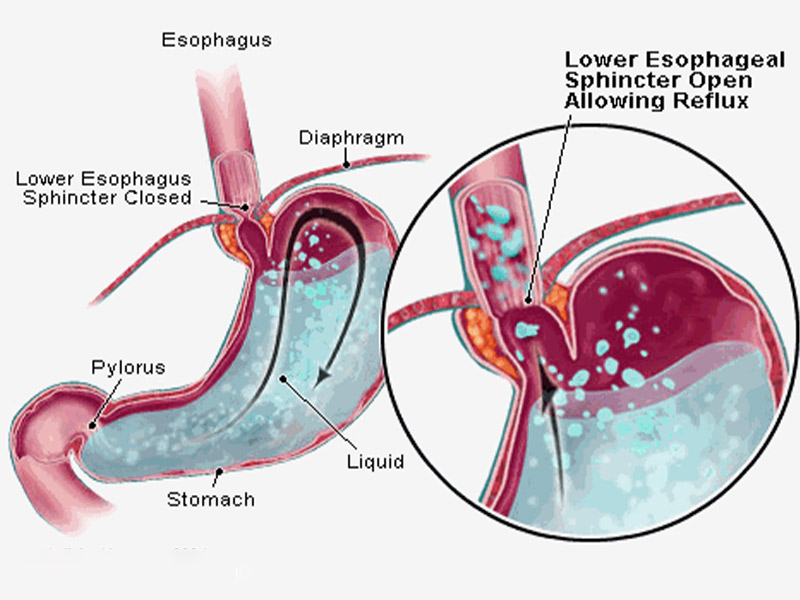
In a healthy person, the lower Esophageal sphincter opens to let the food pass into the tummy, & closes to prevent the gastric juices from backwashing into the Esophagus. In patients with GERD, the lower Esophageal sphincter is weak allowing the back flow of contents from the stomach into the Esophagus.
GERD is a very common digestive problem can be treated through simple lifestyle modifications in most cases.
What are the Symptoms?
Heartburn is the more common symptom of GERD. Apart from Heartburn, patients may also experience:
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Bad Breath
- Breathing Difficulty
- Difficulty Swallowing
What are the Causes?
Acid reflux is very common and occurs in most individuals. This happens due to overeating, sleeping immediately after eating or consuming certain kinds of foods.
However in GERD, which is nothing but recurrent acid reflux has many other causes & risk factors. Some of them include:
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Connective Tissue disorders
- Hiatal Hernia
There are certain factors which can make GERD worse:
- Smoking
- Eating late at night
- Eating certain foods (fatty or fried foods)
- Drinking certain beverages (coffee or alcohol)
- Taking certain medications
How is it Diagnosed?
Your gastroenterologist may recommend several tests to diagnose GERD. Some of them include:
Upper GI endoscopy: This involves inserting a tube with a camera to analyse the esophagus
Upper GI Series: It is a form of X Ray that reveal certain physical abnormalities that lead to GERD
Esophageal pH & impedance monitoring: This test helps in measuring the amount of acid in the esophagus while the patient is eating, sleeping etc.
Esophageal Manometry: This test measures the esophageal contractions while swallowing. It can detect the strength of the sphincter
What are the Risk Factor?
If left untreated, GERD can lead to other serious medical conditions such as:
- Inflammation of esophagus also known as esophagitis
- GERD can lead to Narrowing of esophagus known as esophageal stricture
- Barrett’s esophagus is a condition in which abnormal changes occur in the cell lining of esophagus, eventually leading to esophageal cancer
- GERD can lead to a range of respiratory disorders owing to stomach acids flowing back into lungs. Some of the problems may include asthma, pneumonia & congestion
How is it Treated?
Medications are generally used as the first line of treatment for GERD.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors are generally recommended as they help reduce the amount of acid produced by stomach
- H2 Blockers also help recuse acid production in the stomach
- Antacids counteract acids in the stomach with their alkaline properties. However they tend to cause diarrhoea & constipation in some patients
- Prokinetics are medications that empty the stomach faster. However, their side effects include diarrhoea, constipation & even anxiety