Budd- Chiari Syndrome
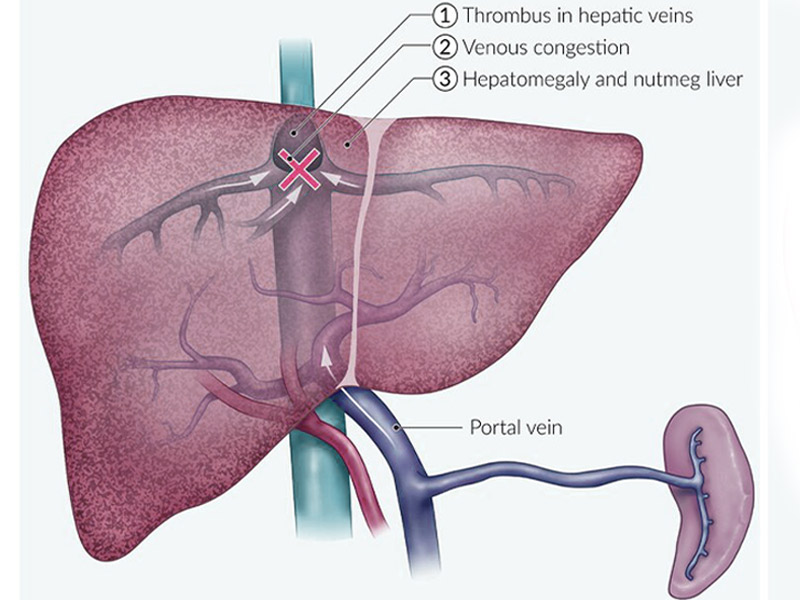
Budd-Chiari syndrome is a condition in which the hepatic veins (veins that drain the liver) are blocked or narrowed by a clot (mass of blood cells). This blockage causes blood to back up into the liver, and as a result, the liver grows larger. The spleen (an organ located on the upper left side of the abdomen that helps fight infection by filtering the blood) may also grow larger.
What are the Symptoms?
The symptoms of Budd-Chiari syndrome include:
- Pain in the upper abdomen.
- Ascites (swelling in the abdomen caused by excess fluid).
- Jaundice (skin, whites of the eyes and mucous membranes turn yellow).
- Enlarged and tender liver.
- Bleeding in the esophagus.
- Edema (swelling) in the legs.
- Liver failure.
- Hepatic encephalopathy (reduced brain functioning caused by liver disease).
- Vomiting.
- Enlarged spleen.
- Fatigue (extreme tiredness).
What are the Causes?
Budd-Chiari syndrome can be caused by conditions and situations that cause your blood to clot (form a blockage). These include:
- Myeloproliferative diseases (those that affect the blood and bone marrow), including polycythemia (the body makes too many red blood cells), and thrombocythemia (the body produces too many platelets).
- Sickle cell disease (a blood disease in which red blood cells change shape from round to sickle-shaped).
- Inflammatory bowel disease (a group of disorders that cause irritation and swelling of the digestive tract).
Pregnancy.
How is it Diagnosed?
Budd-Chiari syndrome is diagnosed through a physical examination and with certain tests. Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and will look for signs of Budd-Chiari, such as ascites (swelling in the abdomen).
Your doctor will also arrange for blood tests to check how well your liver is functioning and to learn if you are at greater risk for blood clots.
Imaging tests will determine if your veins are blocked by clots. These tests include:
- Ultrasound, a procedure that transmits high-frequency sound waves through body tissues. The echoes are recorded and transformed into video or photographs of the internal structures of the body.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan, which uses X-rays and computers to produce images of a cross-section of the body.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a test that uses a large magnet, radio waves, and a computer to produce very clear pictures of the body.
To see if you’ve had cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), your doctor may order a liver biopsy (removal of cells or tissue for examination under a microscope).
What are the Risk Factor?
There are certain conditions that appear to put people at increased risk for Budd-Chiari Syndrome. These include those that cause the body to make too many red blood cells or conditions in which the blood clots too easily.
Budd-Chiari can lead to several liver complications and problems with other body organs and systems.
These include:
- Liver scarring (fibrosis)
- Low liver function
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Gallbladder problems
- Kidney problems
Without treatment, this condition can lead to liver failure in some cases
How is it Treated?
Treatments for Budd-Chiari syndrome are designed to dissolve blood clots and to help improve blood flow in the liver. Treatments are usually drug therapy, non-surgical procedures, and surgery:
- Drug therapy: Your doctor will prescribe drugs to dissolve the blood clots. In addition, the blood-thinning drug is often prescribed to prevent future clots.
- Procedures: There are two non-surgical procedures used in treating Budd-Chiari syndrome:
- transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt and
- percutaneous transluminal angioplasty